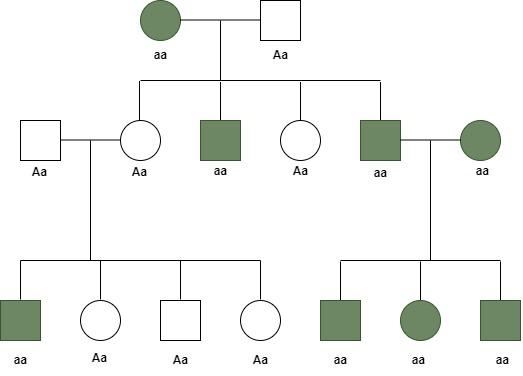
When examining a pedigree chart, it is essential to understand the concept of dominant and recessive traits. Dominant traits are those that are expressed when only one copy of the gene is present, while recessive traits require two copies of the gene to be expressed. For example, if a trait is dominant, it will be displayed in the phenotype even if only one parent carries the gene. On the other hand, recessive traits will only be expressed if both parents carry the gene.
In a pedigree chart, dominant traits are often represented by filled-in symbols, while recessive traits are shown by empty symbols. By analyzing the patterns of inheritance in a pedigree chart, genetic counselors and researchers can determine whether a trait is dominant or recessive and predict the likelihood of it being passed on to future generations.
Pedigree Chart Trait Dorminant Or Recessive
Identifying Dominant and Recessive Traits in Pedigree Charts
One way to identify whether a trait is dominant or recessive in a pedigree chart is to look for patterns of inheritance. Dominant traits will often appear in every generation, as they only require one copy of the gene to be expressed. In contrast, recessive traits may skip generations, as they require two copies of the gene to be displayed.
Another way to determine the nature of a trait in a pedigree chart is to analyze the presence of consanguinity, or the mating of closely related individuals. Consanguinity increases the likelihood of both parents carrying the same recessive gene, leading to the expression of recessive traits in their offspring. By examining these factors, researchers can gain insight into the genetic makeup of individuals and families represented in a pedigree chart.